Smart labels are one of the most common RFID tag types, especially in retail business, but also in numerous applications in other industries. Increasing acceptance of RFID and the double-digit growth rate of inlay/tag volumes in the past years have made smart labels an attractive business segment not only for the established RFID companies, but also for the traditional label manufacturers.
The barrier for a label company to enter the RFID/smart label business is very low as their core business comprises of printing and converting anyways – adding “inlay insertion” or “inlay lamination” to the converting process will increase the label manufacturer’s value-add and enables meeting the customers’ RFID and IoT requirements.
The Smart Label Opportunity
Label market is a big business, but expected to grow only a few percent a year, which is roughly double compared to print market in general though. The big opportunity lies in smart labels where CAGR of 15 to 20 percent is expected in the coming years, thanks to continuous tag cost reduction and huge amount of new application areas utilizing RFID technology.
Retail industry has been working long and very hard to utilize RFID technology and counts for the biggest tag volumes as of today. If one of the initial drivers justifying RFID in the early days was efficiency improvement in logistics, today there is an increasing number of drivers and quantified value-add right next to the consumers:
- Integrated customer experience in omni-channel environment
- Customer engagement and consumer interaction
- Unmanned stores
- Freshness and cold-chain tracking
- Labeling obligations by authorities
- Anti-counterfeiting measures.
RFID is the dominating technology today in smart labels, and RFID labels are successfully used to address all the requirements mentioned above. The big volumes of smart labels are typically produced by key players in RFID industry, i.e. either inlay/tag manufacturers or converters, however there are also several smart label producers focusing on specialized tags and applications. Integrated part of the smart label business are also the value-add services like tag performance testing and encoding of product and supplier specific information in each tag.
The current suppliers will certainly increase their capacity as the demand grows, but at the same time there is an opportunity window open for new entrants to take their share of the smart label market and related services.
How to Make Your Labels Smart?
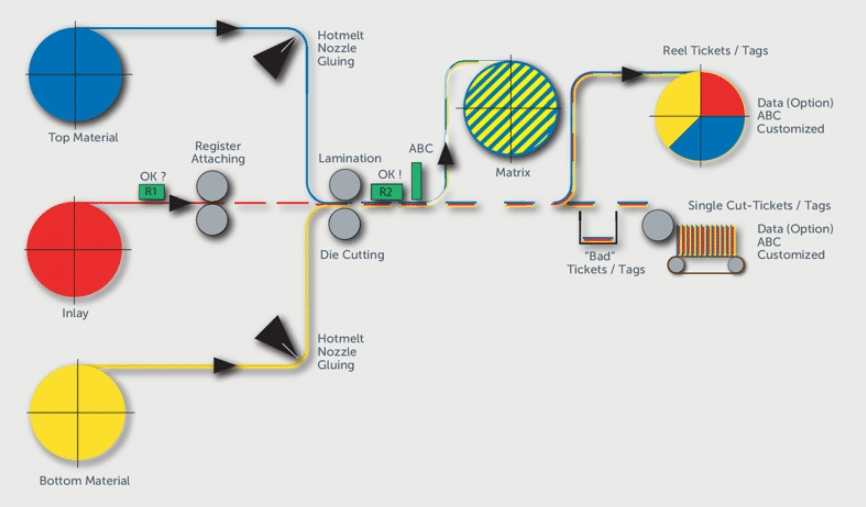
Smart labels based on RFID technology (RAIN and/or NFC) are produced with a dedicated converting machine laminating the RFID inlays between the top material and the liner as shown in image below.
The selection of suitable RFID inlay type and supplier would be based on the RFID application and customer specification or alternatively smart label manufacturer’s own specification. Below image by permission from BW Papersystems, from their Speedliner RFID Converting machine brochure, illustrates RFID converting principle:
It is not only about manufacturing though, as smart label production brings also new requirements for the process:
- Functional and/or performance testing to manage the RFID tag quality
- Encoding capability to store customer-specific data in each tag.
The good news is that these capabilities can be integrated into converting machines and they create a value-add service opportunity. Smart labels can be an entry point to the RFID value chain for a traditional label company with increased turnover and profits.
Testing and Encoding Added-value
With the increasing tag volumes and adoption of RFID, the demand for RFID testing has grown even faster. This is caused by the fact that many RFID applications are fully integrated into various business processes where the basic requirement is that each tag can be read reliably every single time in the field – otherwise the efficiency of the process would collapse.
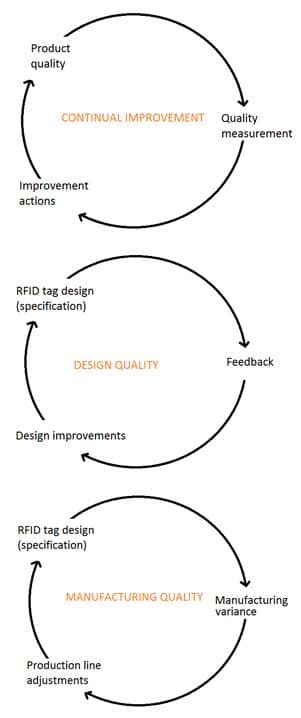
Accordingly, the RFID end-users are setting more requirements for quality assurance in RFID production and demanding actual performance measurement instead of simple pass/fail testing by RFID readers.
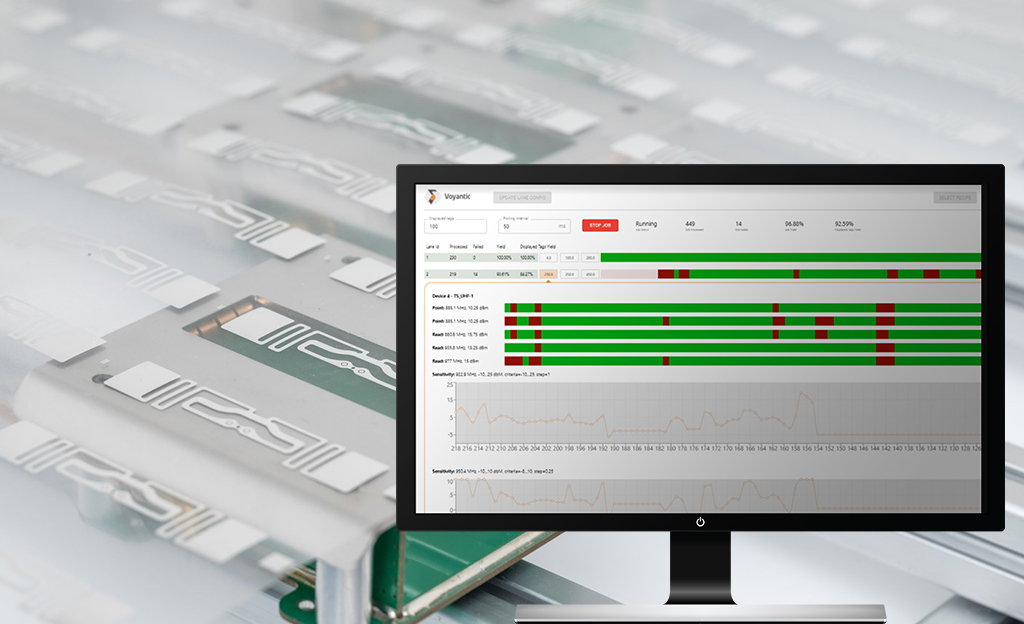
RFID Performance Testing
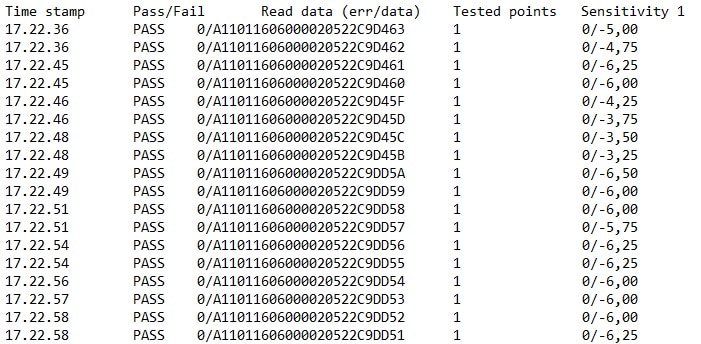
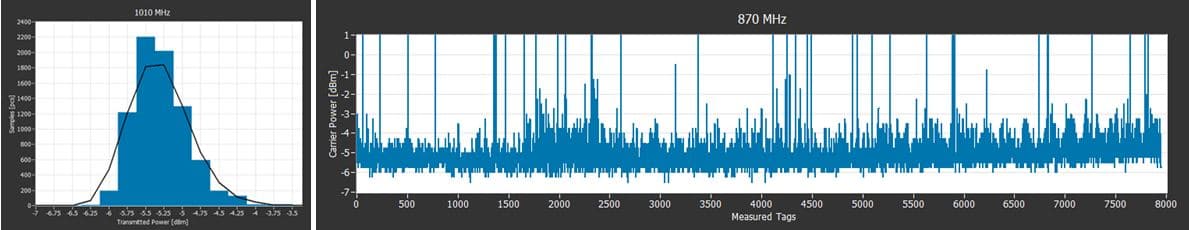
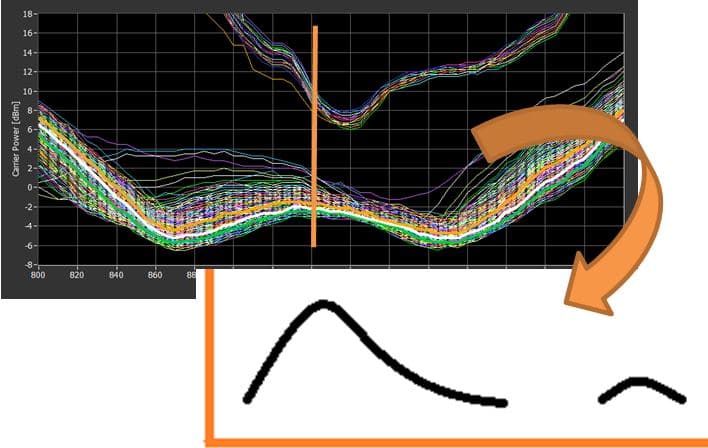
Ensuring high smart label quality (= successful read in the field) requires more than simple pass/fail testing with an RFID reader. More reliable performance testing can be done by measuring the tag sensitivity in the production line with variable power levels and several frequencies using an RFID production testing system.
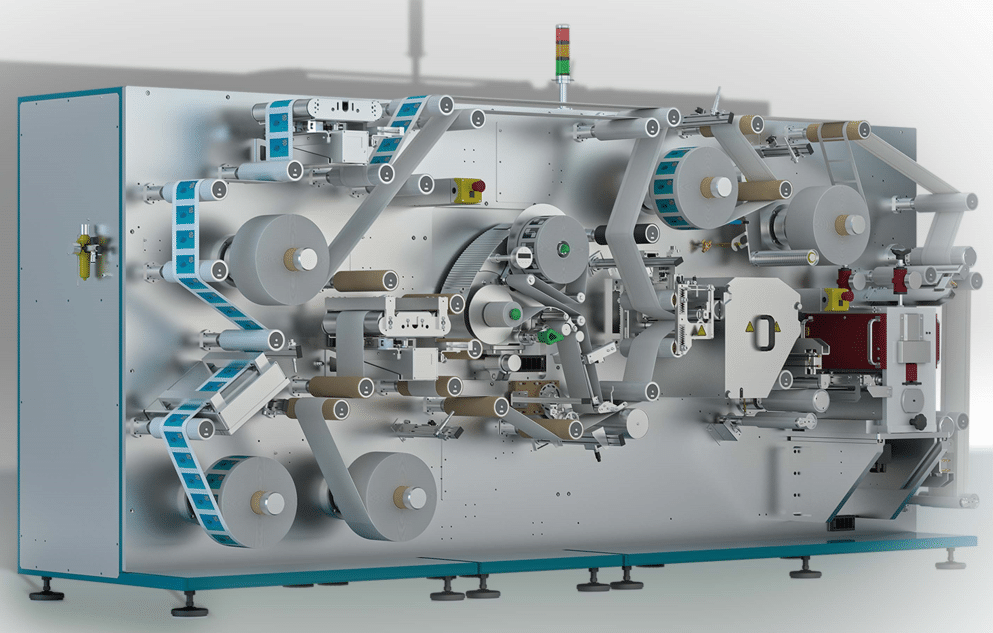
Voyantic Tagsurance inline production testers can be used in single and multi-lane configurations integrated with various third-party RFID machines, like Mühlbauer CL Light RFID Converting Line pictured here.
The same Tagsurance solutions are also available for Voyantic Reelsurance and several 3rd party offline test machines for sample testing of finished labels or incoming inspection of the outsourced RFID inlays.
Encoding and Personalization
New requirements are set also for encoding functionalities as new RFID applications and users are emerging. There is a growing need for managing deliveries of special tags with customer specific memory content, often with short delivery time and rather small batches. Encoding functionality can be integrated either in converting machines or alternatively done in dedicated offline personalization machines.
How To Learn More?
If you are considering making your labels smart, please contact us to schedule an online meeting to discuss your needs. You can also learn more about our production testing solutions and reach out to us to learn more about Voyantic solutions with our machine vendor partners.
All blog posts