Last year, we teamed up with TSC Printronix Auto ID and started a webinar series designed for barcode professionals, who are considering expanding their offering to RAIN RFID labels, or who already are at the beginning of that journey. With TSC Printronix Auto ID we saw the need for education as more and more barcode label customers are looking for RFID solutions.
In the first webinar, What a barcode professional needs to know about RAIN RFID Label and Tag Data, we started from the basics: what are the key aspects of RAIN RFID technology and data, how does RAIN RFID actually work, what are the system components, and most importantly, where can you find more information.
The second part of the webinar series, What a Barcode Professional Needs to Know about the RAIN RFID Encoding Processes, focused on the practicalities of the RAIN RFID encoding process, equipment, and alternatives.
In the third webinar, What a Barcode professional needs to know about RAIN RFID label selection and sourcing, scheduled for February 10th, we will cover the most important considerations related to label selection and sourcing process including label specifications, supplier selection, delivery format, handling, and other issues.
Here are my main takeaways from the first two webinars in the series.
Key Takeaways from Part 1
It is crucial to understand filtering in the context of RFID systems
The nature of RF signals means that they can go through walls and various other materials. A RAIN RFID reader can read a large number of tags simultaneously and without a line of sight, which is, in comparison, required for reading barcodes. For example, when you are inventorying tagged items in storage, your system could be reading tags behind a wall that should not be included in your inventory. Setting up tag filtering correctly ensures that your application works accurately, and that requires following proper data encoding processes.

There is no “one size fits for all” RAIN tag
What do you need to know about RAIN RFID tags when looking for a tag for your customer? The difference between a barcode label and an RFID label is that the RFID label includes an IC (microchip) and an antenna. Together the IC and the antenna make up an RFID inlay. There are lots of different IC models out there and the type of IC defines what kind of and how much data can be encoded in the tag. The antenna model defines how far the label can be read. Knowing your solution requirements, physical factors such as the label size and item materials, and use cases and data requirements are necessary for finding the best tag for your solution.
Do not use a proprietary numbering system
Keeping the importance of filtering in mind, it is crucial to understand the basics of RAIN RFID encoding systems, i.e., how you are putting data into a tag. There are three data standard families available for RAIN RFID tag encoding
- GS1 EPC tag data standard
- ISO/IEC data standards
- RAIN numbering system, a subset of the ISO standard
Following one of the established data standards ensures there won’t be issues with tag filtering (and application errors) along the road.
The fourth option is to use your own proprietary encoding systems – Please do not do it! Or if you do, you need to “wrap” your system within the ISO standard or the RAIN numbering system.
Selecting the data standard to use often depends on your customer or the industry you are operating in. Some customers may mandate that you use a specific standard, and many industries have a mandated or de-facto standard in use to ensure interoperability.
Above are my key learnings of Part 1, but many more topics and details were discussed. Watch the webinar to learn more about each of the data standard families, including the structure of the different numbering systems and example use cases, as well as the basics of data security. Webinar part two dives deeper into the standard selection process and the specific advantages of the different standards.
Key Takeaways from Part 2
Label Manufacturing Process
The label manufacturing process includes three steps. In the first step, the IC is attached to the antenna, creating an inlay. In the second step, the inlays are converted in a common backing material called a liner, creating a blank label. In the third step, data is printed on and encoded into the label, creating a finished label.
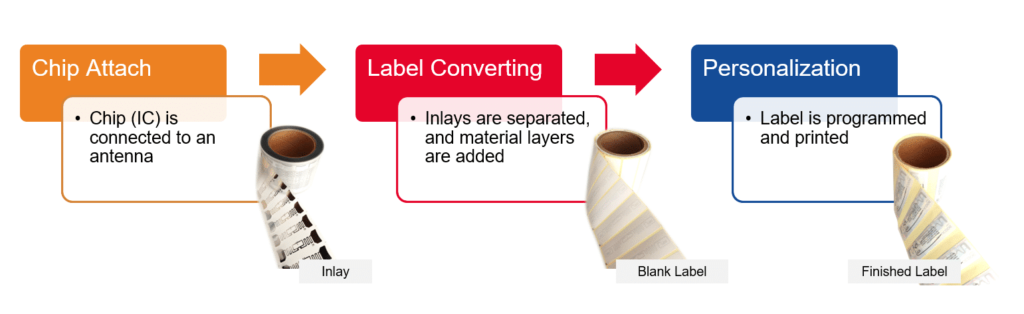
While the process itself is simple, the manufacturing machines are quite complex. Watch the webinar to learn more ›
- Additional reading: https://voyantic.com/blog/posts/rain-rfid-on-label-processing-machines-an-overview-to-help-with-your-choices/
Encoding Equipment Types and Process
The suitable type of encoding equipment depends on the volume of tags that need to be encoded. The more sophisticated machines that can process high volumes at high speed naturally come with a higher cost.
An RFID reader can be used as an encoder but it is not an efficient permanent solution.
An RFID printer is purpose-built for encoding and is best suitable for small rolls and batches. They can be affordable and process up to some thousands of labels per hour.
High throughput personalization machines can take in larger rolls and process up to one hundred thousand tags per hour, but they also come with a higher cost.
And finally, encoding can also be integrated into product production or packaging lines.
Watch the webinar recording to dive deeper into the IC selection factors, encoding process steps, RAIN tag memory details, as well as tag locking and passwords – ensuring the right data is encoded in the right way.
The Personalization Process
The personalization process includes both printing data on the label and encoding the tags. The printed data can be the same data that’s in the RFID tag or include additional information.
High throughput personalization lines often process labels in successive stations. Combining the print and encoding in a high-speed personalization process requires accurate triggering for all the steps and making sure the stations match the process flow.
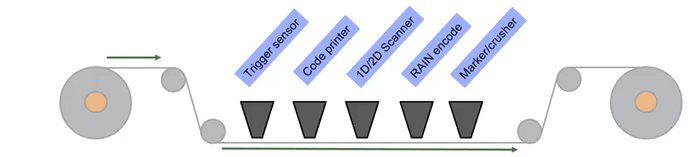
Using an RFID printer for personalization is a good option for smaller-scale projects. An RFID printer prints the barcode and other designed details on the label as well as encodes and verifies the RAIN tag data.

Part 3: RAIN RFID Tag Selection and Sourcing
Learn the most important aspects of label selection and sourcing, including label specifications, supplier selection, and delivery format.
