Identification of tires has been one of the early use cases of RAIN RFID already back in 2005. It took almost ten years for the technology and value chain to mature to a state when this extremely challenging application became finally possible.
Million Reasons to Tag Tires
There are countless ways to utilize RFID enabled tires. Early deployments follow the use cases familiar in the generic retail business: improving the traceability in the supply chain and raising efficiency in warehouse inventory and management. Over time I bet we will also see use cases after distribution, such as tire fleet management, safety monitoring (pressure, wear, retreading), and eventually even in recycling.
Once tires are RFID enabled, it opens enormous possibilities for companies to streamline processes and even create new business models.

“Scrapping a Finished Tyre is Not an Option”
If an embedded RFID tag is defected, it cannot be replaced with a new one because of safety and practical reasons. At the same time, no manufacturer is willing to scrap a new baked tire because of a non-functional RFID tag. Is there a way to avoid such a situation?
A carefully implemented quality monitoring helps keep the tire manufacturing process lean and efficient. RFID is implemented in various ways within the tire industry. Thus, preparing the tagging specifications according to actual use cases of the complete value chain is a prerequisite. Read more of this framework:

What is the Framework of RFID Tagging in Tire Industry?
Learn how to prepare tagging specifications according to actual use cases of the complete value chain!
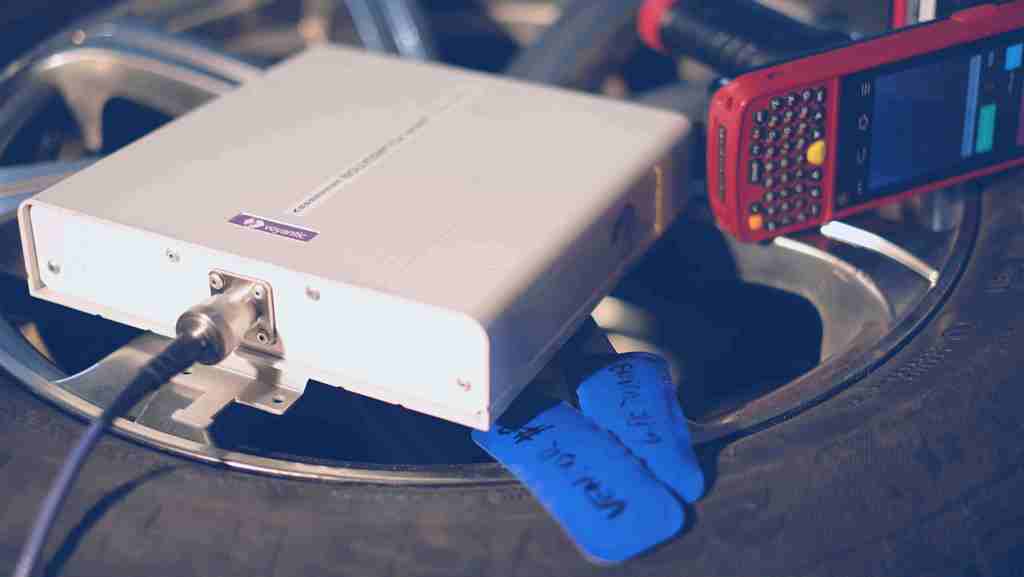
Embedding RFID UHF Tag into Rubber and RF Testing
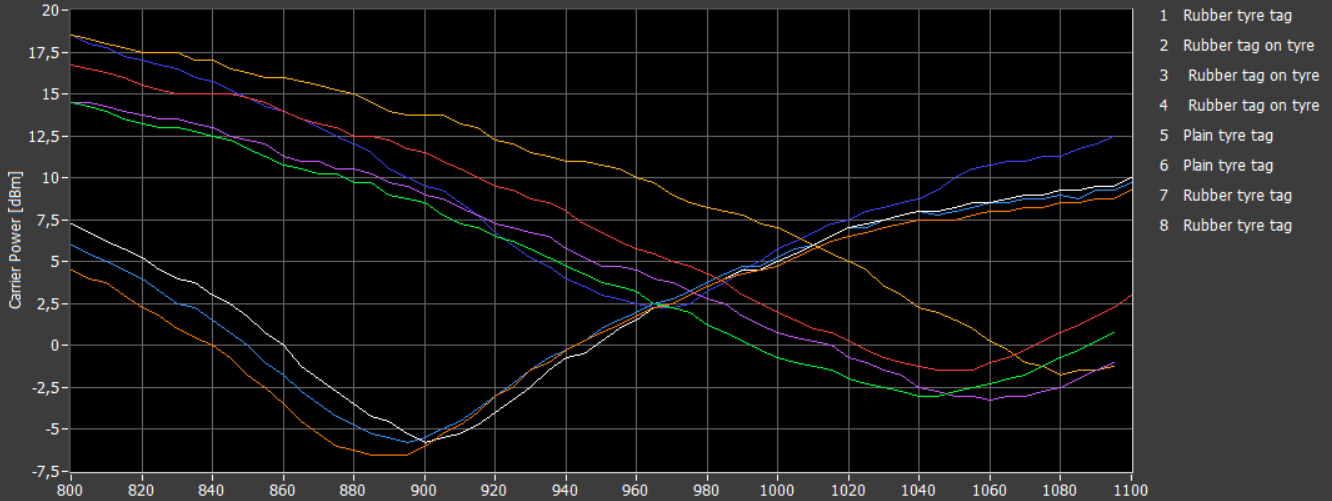
Before embedding in rubber, the tire tags are tested in free-air conditions. UHF tire tags are typically over tuned to frequencies over 1 GHz. This makes RF testing a challenge because standard RFID readers operate at frequencies below 1 GHz.
From the manufacturing standpoint, additional requirements include:
- individual tag test should be wireless;
- test may be performed on trays with a large number of other tags in close proximity;
- the production flow cannot be slowed down.
The Voyantic solution is to utilize Tagsurance RFID tester together with the Snoop Pro near field coupling element. This enables accurate READ sensitivity tests for the complete dipole tag structure with excellent correlation to far-field performance.
RF testing used to be one of the bottlenecks in the tire tag production process. However, the sophisticated test features of the Tagsurance tester mean that the slowest processes are the mechanical ones.
Please read of our testing solution in more detail from our customer case study Michelin – Tire Tags with Consistent Quality!
Industry-Wide ISO Standards in the Horizon
The industry is currently waiting for the work group to finalize following standards, like
- ISO/CD 20909, Radio frequency identification [RFID] tyre tags
- ISO/CD 20910, Coding for radio frequency identification [RFID] tyre tags
- ISO/NP 20911, Embedding methods for radio frequency identification [RFID] tyre tags
- ISO/NP 20912, Testing methods for radio frequency identification [RFID] tyre tags
For an update on the ISO standards process, please stay tuned for an upcoming blog from Juho Partanen later this year.
If you’d like to hear how Voyantic can enable you to perform tire RFID testing in your facility, just drop us a line – it will be my pleasure to walk you through the process!
All blog posts